Storytelling in Product Marketing: How to Connect with Your Audience

In a world where customers are inundated with information, storytelling has emerged as a powerful way to connect with your audience and differentiate your product. Stories evoke emotions, build trust, and make products memorable, transforming them from mere commodities into something customers can relate to on a personal level. This article explores the art and […]
How to Build a High-Performance Sales Culture in Startups

Building a high-performance sales culture in a startup is one of the most critical factors for sustained growth. With limited resources and immense pressure to scale quickly, startups must cultivate a culture that motivates, retains, and empowers top sales talent. This article explores the key strategies to create an environment where sales teams thrive and […]
Identifying New Markets: When and How to Expand

Expanding into new markets is a significant growth strategy for businesses looking to scale. However, venturing into unknown territories requires careful planning, market research, and strategic decision-making. This article provides a step-by-step framework for identifying new markets and determining the right time and approach for expansion. 1. Recognize the Right Time to Expand Expanding too […]
Cold Outreach Mastery: Crafting Emails and Messages That Get Replies

Cold outreach can be a powerful tool for driving business growth, but it often gets a bad reputation due to spammy, impersonal messages. When done correctly, cold outreach can open doors to valuable opportunities and partnerships. This article breaks down how to craft emails and messages that not only get opened but also earn meaningful […]
The Future of Networking: Using Digital Platforms for Business Growth

In today’s hyperconnected world, networking has evolved far beyond traditional handshake meetings at conferences or networking events. Digital platforms now dominate as the primary avenues for forging business connections, enabling professionals to expand their networks globally without leaving their desks. For startups and businesses, understanding how to leverage these platforms is critical for growth. Here’s […]
Scaling Sustainably: Aligning Business Development with Long-Term Goals

For businesses aiming to scale, rapid growth often takes center stage. However, pursuing expansion without considering long-term sustainability can lead to resource strain, operational inefficiencies, and even failure. Aligning business development strategies with sustainability principles ensures that growth is not only achievable but also enduring. Here’s how companies can balance scaling with long-term objectives. 1. […]
Sales Automation on a Budget: Tools and Tips for Startups

For startups, scaling sales processes without breaking the bank is a delicate balancing act. Sales automation can help streamline operations, improve efficiency, and maximize your team’s productivity—all without requiring a hefty investment. Here’s how to implement sales automation on a budget and the tools you need to get started. 1. Why Sales Automation Matters for […]
Creating Feedback Loops: How to Use Customer Insights for Better Product Marketing
In today’s competitive marketplace, understanding your customers isn’t just a nice-to-have—it’s essential for effective product marketing. Feedback loops allow businesses to continuously gather insights, refine strategies, and ensure their messaging aligns with customer needs and expectations. Let’s explore how to create and use feedback loops to supercharge your product marketing. 1. What Are Feedback Loops? […]
Growth Hacking for SaaS: Unconventional Marketing Tactics to Drive Exponential Growth

In the highly competitive world of Software as a Service (SaaS), companies are constantly seeking ways to accelerate growth while keeping costs low. Traditional marketing methods are often not enough to stand out in this fast-paced industry. Enter growth hacking: a combination of creativity, analytics, and experimentation that focuses on rapid growth. Growth hacking for […]
Building a Scalable SaaS Marketing Funnel: From Awareness to Conversion
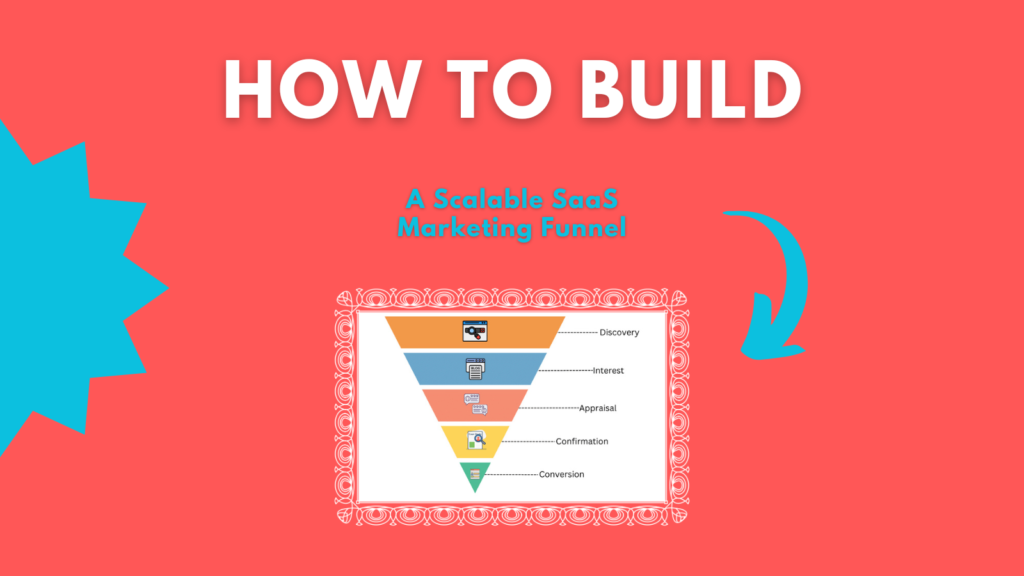
Creating a marketing funnel that guides potential customers from awareness to conversion is crucial for success. SaaS businesses face unique challenges in marketing due to their subscription-based model, long sales cycles, and the need for strong customer retention. This article will guide you through building a scalable SaaS marketing funnel that addresses these challenges, helping […]